Light steel or wood-which frame is better in residential construction?
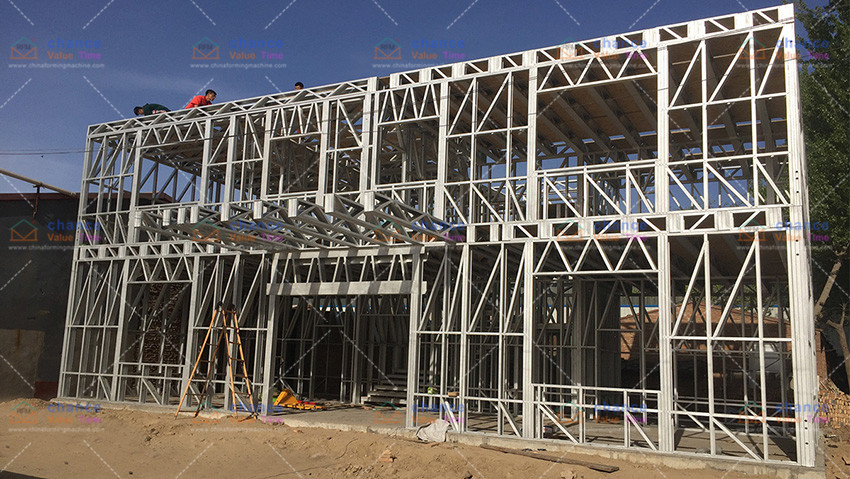
If you plan to build a house, your research may lead you to start using light steel (LGS)-a slowly emerging alternative to timber frames. It is sturdy, durable, flammable, flexible in design, and performs well in natural disasters. Having said that, LGS is struggling to gain appeal as a housing frame material, partly because of its high cost and poor heat resistance.
If you decide whether to use tested timber to frame your house or the LGS, which may be more expensive but more expensive, consider the following questions:
Which material is more durable?
Which performs better in earthquakes, fires and floods?
What can help me reduce energy costs?
Which is cheaper and faster to install?
Which of the above factors are most important to me?
These key decision factors are summarized below.
1. Durability
wood
The durability of wood comes from its ability to match the moisture content of the surrounding air. Even if it is soaked in water, as long as it is drained, the wood can still be dried without any problem. This ability to absorb and release moisture allows wood to perform well in climates with high relative humidity.
Although moisture can be released under appropriate conditions, the wood will suffer severe damage if it is soaked for a long time. Mold will form and spread, causing the wood to rot. The recent tragedies in Berkeley and Folsom are prime examples of structural damage caused by the continuous exposure of wood components to moisture.
Termites are another enemy of wooden structures. The cellulose content of wood attracts underground pests, and once they enter the house through various gaps, they will attack any wooden objects in the path. The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) estimates that the annual property damage caused by termites is worth more than $2 billion.
Despite these weaknesses, wooden frames can last a long time. Take the Fairbanks Tower as an example. Built around 1641, this house is located in Massachusetts and is the oldest wooden structure in the United States. In the late 19th century, many houses built with balloon frames that are now outdated are still today.
LGS
In terms of durability, steel has advantages over wood. The inorganic properties of steel protect it from mold, rot and pests. Steel is non-porous, does not accumulate water, and does not suffer from moisture-related warping, shrinkage or cracking. In other words, exposure to water and salt air will cause corrosion of LGS components, and appropriate anti-corrosion measures must be taken to deal with it.
2. Seismic performance
wood
Wood is a strong material. Normally, the wooden frame transfers the vertical load along the studs to the concrete foundation below. When an earthquake occurs, horizontal loads begin to act on the structure. In order to prevent collapse, it must be supported by sufficient lateral stiffeners. By connecting wooden structural panels to the frame to form a shear wall, lateral support can be achieved, and there are other options including prefabricated shear walls.
LGS
In terms of resistance to lateral loads, the design flexibility of steel is its main advantage. Where seismic support options for wood frames are usually limited to shear walls, LGS frames provide engineers with multiple options. These include flat X-shaped supports, plywood and steel sheaths.
3. Fire resistance
wood
Nowadays, pine, fir and spruce have become the preferred tree species in timber construction. Inexpensive, lightweight, these types are economical and easy to operate during installation. Unfortunately, their softwood ignites quickly and spreads flames faster than the heavy hardwoods that were once popular in timber frames.
In order to prevent the wood structure from burning, the design must incorporate refractory
materials, such as fire-resistant gypsum wallboard, as well as a sprinkler system, and sufficient exits and exit routes.
LGS
The flammability of steel hinders the spread of flames, which is an important safety feature lacking in wooden frames.
Although it does not burn, once exposed to temperatures above 550°F, steel does begin to lose strength. Residential fires hover around 1,100°F. At this temperature, steel retains only 50% of its normal yield strength. Without proper protection, the steel frame would bend and collapse. To prevent this from happening, refractory materials must be used to prevent the frame from being directly exposed to the flame.
4. Flood disaster
wood
As long-term soaking in water, wood will mold, rot, warp and shrink, so flood prevention measures should be taken when building houses in areas prone to floods. Use anti-expansion paint, expand polystyrene (XPS) heat insulation board to coat waterproof coating on the frame, and spray high-density closed-cell foam on the stud bracket, all of which prevent or reduce the wooden frame of the building. Effective measures for flood damage.
LGS
Galvanized steel has a zinc protective layer, which can be used as a moisture barrier. This coating gives galvanized steel an absolute advantage over wood, which makes it almost invincible under flood conditions.
It should be noted that the quality of protection provided by galvanizing depends on the thickness of the coating and environmental conditions. Galvanized steel exposed to salt air, acid, strong alkali, and prolonged immersion in water may lose its zinc coating and begin to corrode over time. In this unfavorable environment, the service life of steel may benefit from the corrosion protection layer on top of the galvanized layer.
5. Energy efficiency
Thermal bridging is a process by which heat can escape the enclosed space by bypassing the insulating material.
The chemical properties of steel make it an excellent thermal bridge. Its electrons move freely, and when they gain energy by being exposed to heat, they begin to vibrate rapidly and transfer energy to neighboring electrons.
The heat transfer rate of steel is much higher than that of wood, and the overall R value of the
wall can be greatly reduced without additional heat insulation and special assembly design.
In order to prevent heat loss in light steel wall components, a rigid insulation board and dry wall should be placed on the outside of the studs. This keeps the stud on the hot side of the insulator and prevents heat dissipation.
The wooden frame is non-thermal, so it is much easier to meet the specified R-value requirements. Since heat transfer relies on molecular vibrations and collisions, porous materials including wood are poor heat conductors. In a typical wood frame assembly, there is no need to insulate the frame of the building.
6. Cost
The low price of wood is the main reason why wood frames are popular despite many defects.
In a study conducted by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development, three pairs of houses were built. Except for the frame materials, each pair is the same-one house has a wooden frame and the other has a light steel frame. The study concluded that the price of steel structure houses is 14.7% higher than that of wood structure houses. The experiment did not consider the additional insulation required by the steel frame.
7. Timetable
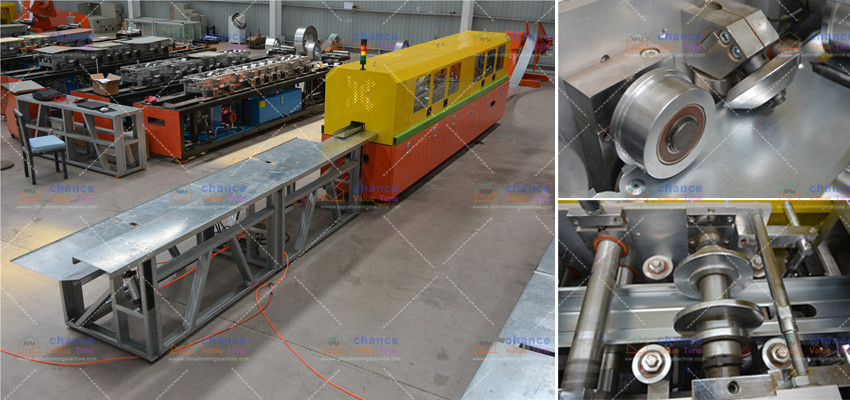
Time is money, and the length of the project schedule may have a direct financial impact on the owner and the builder. Although many people claim that steel can be installed faster than wood, all variables that affect installation time must be considered before accepting such statements.
One of these variables is the installer’s familiarity with the LGS framework, because skilled drafters may take longer to complete the phases of the project. Currently, steel is not popular in single-family housing frames, and not all house builders have experience in using it. Similarly, although steel is lighter and requires less site preparation, the delivery date of steel cannot be predicted, depending on availability and design complexity.
in conclusion
As a frame material, LGS is superior to wood in many aspects. It will not produce mold, rot or be crushed by termites like wood. The strength of steel and the versatility of design make it an excellent frame material in areas prone to earthquakes, and its excellent durability can protect steel from flood damage. Despite the higher cost, the high strength-to-weight ratio of steel means that the stud spacing can be 24 inches instead of 16 inches, saving materials and labor.
But steel also has its weaknesses. In a fire, its flammability can be offset by the tendency to lose strength and bend at high temperatures. Because of this feature, once they learn that the building is a steel structure, some fire departments restrict their fire fighting work to the outside of the building.
Steel’s poor performance in preventing heat transfer is another flaw that has contributed to the material’s poor reputation. This is usually a big problem for homeowners who want to limit energy use and those who worry about their heating and cooling costs.
These factors, combined with higher upfront costs, constitute an obstacle to the acceptance of steel in mainstream residential construction. So far, wood continues to dominate the market due to its low cost, reliable durability, and long history of being the frame material of choice.
How we can help
If you are not sure which frame material is more suitable for your project, Liming can help you. Our engineers can evaluate your design intent and propose cost-effective framework solutions.
If you choose to use wood or LGS as the frame material, our team will work with your architect and all related disciplines to provide a structural design suitable for your building.74